📖 Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision, 2021.
0. 요약
- 기존 연구
- 미리 결정된 객체를 예측하도록 훈련
- CLIP이 기존 연구와 다른 점
- 이미지에 대한 원시 텍스트 학습을 통해서 더 광범위하게 학습함.
- 인터넷으로 수집한 4억 쌍의 이미지-텍스트 데이터 세트로 훈련
- 사전 훈련 후 다운스트림 작업 가능
- zero-shot transfer
- 모델은 대부분의 Task에 non-trivially하게 transfer
- 특수한 데이터 셋으로 훈련하지 않아도 지도학습과도 경쟁력있는 성능
1. Introduction and Motivating Work
- text-to-text
- NLP 모델은 web-scale
- Vision : crowd-labeled dataset (ImageNet 등)
= 웹 텍스트 사전학습 방법을 vision에 적용?!
- 이전 모델
- (1999) 문서의 명사와 형용사 - 이미지 pair 학습
- (2007) predict words in caption associated with images
- (2012) low-level image and text tag features
- (2016) CNNs trained to predict words in image captions
- (2016) YFCC100M dataset : multi-label classification task (AlexNet 기반)
- (2017) Imagenet …
- (2020) VirTex, ICMLM, Con-VIRT 기반 모델 등장 (contrastive objectives to learn image representations from text)
- CLIP 특징 및 본 논문에서 다루는 것
- 대용량 이미지로 훈련 (웹 기반) : 4억
- Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training
- 30가지의 데이터 셋으로 테스트 - 테스크에 구애받지 않고 좋은 성능을 보임
- zero-shot 으로 수행한 분류 테스크에 대해서 기존 지도학습 보델보다 성능 좋음
2. Approach
2.1 Natural Language Supervision
- 자연어는 확장하기 쉽다. 방대한 양의 텍스트에 포함된 형태로 수동적으로 배우도록 함.
2.2 Creating a Sufficiently Large Dataset
- 자연어 데이터의 주 동기는 “많은 양의 공공 인터넷 데이터”를 사용할 수 있다는 것.
- 인터넷에서 공개적으로 사용할 수 있는 4억쌍 데이터셋 구성.
- (이미지, 텍스트) 쌍을 검색 → 500,000개의 쿼리 집합 이용했고 쿼리당 최대 20,000개로 클래스 균형을 조정 (WebImageText)
2.3 Selecting an Efficient Pre-training Method
- 첫 시도 : VirTex (jointly trained an image CNN and text transformer from scratch to predict the caption of an image) → 개선 X
- ResNet-50 image encoder 기존 모델보대 3배 느림
- 분류기는 정확한 단어를 예측하려고 함 → 어려움.
- 대조적 표현 학습을 통해서 더 나은 표현 가능
- 고품질 이미지 표현 학습 가능하나 컴퓨터 자원이 몇배 필요함.
- bag-of-word 단위
- N(이미지, 텍스트) 쌍 배치가 주어지면 CLIP은 배치 전체에서 N × N 가능한 (이미지, 텍스트) 쌍 중 어떤 것이 실제로 발생했는지 예측하도록 훈련
- CLIP는 이미지 인코더와 텍스트 인코더를 공동으로 훈련시켜 N개의 실제 쌍의 이미지와 텍스트 임베딩의 코사인 유사성을 극대화 ↔ N^2-N 개 잘못된 쌍의 임베딩 코사인 유사도 최소화
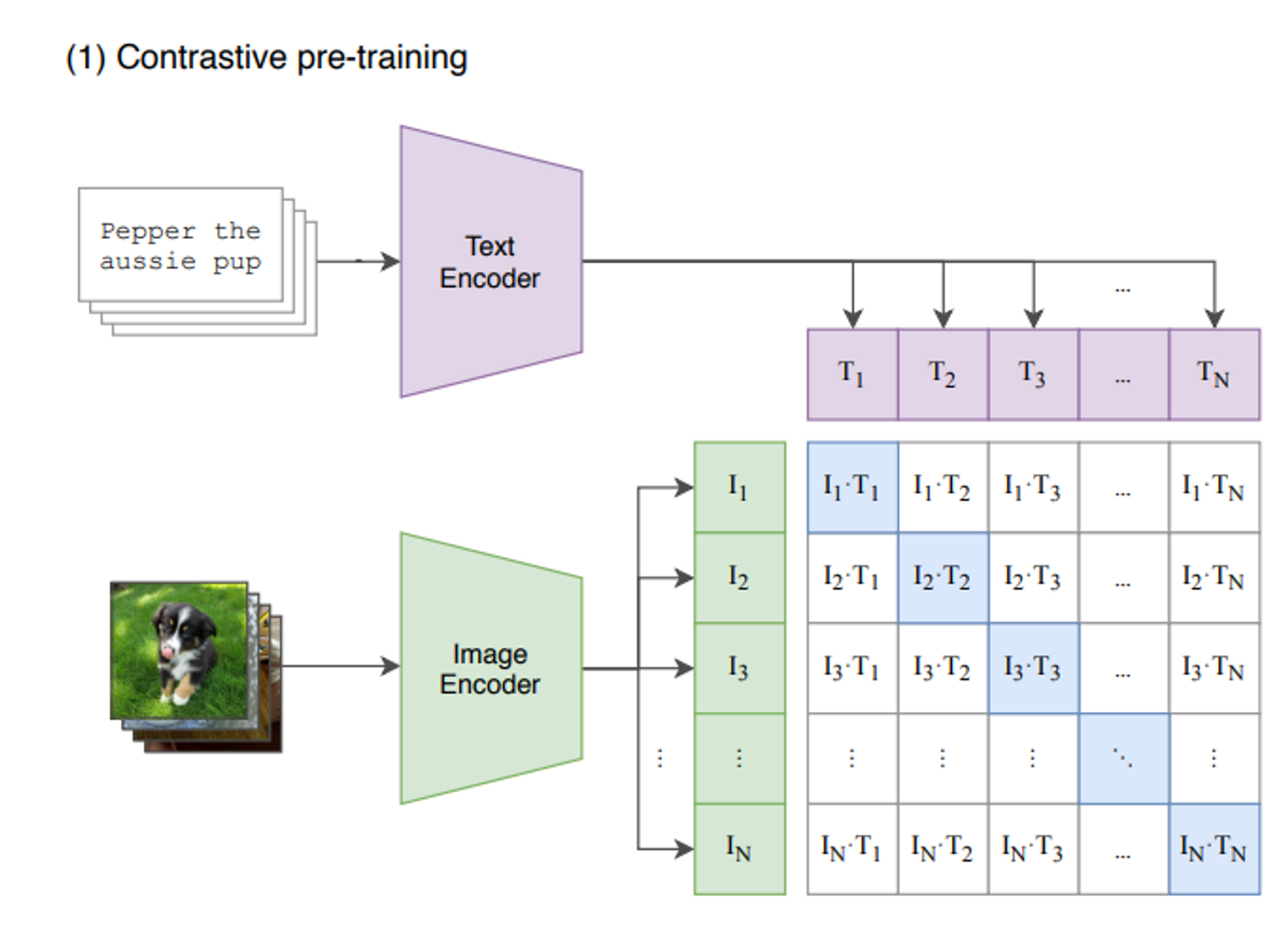
- CLIP은 데이터 세트가 커서 overfitting이 발생하지 않음. (주요 문제는 아님). 비선형 방식도 사용하지 않음.
- We train CLIP from scratch without initializing the image encoder with ImageNet weights or the text encoder with pre-trained weights.
- psudocode

2.4 Choosing and Scaling a Model
- 이미지 인코더
- ResNet-50
- ResNetD 개선, antialiased rect-2 blur pooling, global average pooling layer with an attention pooling, attention pooling is implemented as a single layer of “transformer-style” multi-head QKV attention
- Vision Transformer (ViT)
- We closely follow their implementation with only the minor modification of adding an additional layer normalization to the combined patch and position embeddings before the transformer and use a slightly different initialization scheme.
- transformer 이전에 결합된 패치 및 위치 임베딩에 레이어 정규화를 추가하는 수정만 했음.
- ResNet-50
- 텍스트 인코더 (깊이 조정X)
- Transformer
- As a base size we use a 63M-parameter 12-layer 512-wide model with 8 attention heads.
- The transformer operates on a lower-cased byte pair encoding (BPE) representation of the text with a 49,152 vocab size
- [SOS] [EOS] 토큰 표현
- Transformer
2.5 Training
- 5 ResNets and 3 Vision Transformers 훈련
- RN50x4, RN50x16 및 RN50x64
- ViT-B/32, ViT-B/16 및 ViT-L/14
- Adam Optimizer & cosine schedule
- RN50x64는 592개의 V100 GPU에서 교육하는 데 18일 소요
- 최대 규모의 Vision Transformer는 256 V100에서 12일이 소요
3. Experiments
3.1 Zero-Shot Transfer
1) Motivation
- task-learning에 초점을 맞춤 (evaluates performance on a task on a specific distribution)
- 시각 N-그램(Visual N-grams)
- N-그램은 원래 자연어 처리에서 사용되는 것으로, 주어진 텍스트에서 n개의 연속된 요소(단어 또는 문자)로 이루어진 시퀀스를 의미.
- 컴퓨터 비전의 맥락에서 시각 N-그램은 이미지에서 추출된 시각적 요소 또는 특징들의 연속된 시퀀스를 말함.
2) Using CLIP for zero-shot transfer
- we use the names of all the classes in the dataset as the set of poten- tial text pairings and predict the most probable (image, text) pair according to CLIP.
3) Initial comparison to Visual N-Grams
- 동일한 조건에서 훈련한 것이 아니므로 동일한 선상에서 비교하기에는 어려움.
- In total we expand from the 3 datasets reported in Visual N- Grams to include over 30 datasets and compare to over 50 existing computer vision systems to contextualize results.
4) Prompt engineering and ensembling
<문제>
- A common issue is polysemy. When the name of a class is the only information provided to CLIP’s text encoder it is unable to differentiate which word sense is meant due to the lack of context. In some cases multiple meanings of the same word might be included as different classes in the same dataset!
- Another issue we encountered is that it’s relatively rare in our pre-training dataset for the text paired with the image to be just a single word. Usually the text is a full sentence describing the image in some way.
<해결방식>
- To help bridge this distribution gap, we found that using the prompt template “A photo of a {label}.”
- “A photo of a {label}, a type of pet.”
- “a satellite photo of a {label}.”
- ”A photo of a big {label}” and “A photo of a small {label}”.
5) Analysis of zero-shot CLIP performance

- 27개 데이터셋에서 16개가 더 높은 성능
- ImageNet의 명사 중심 < 동사를 포함하는 시각적 표현 더 높은 성능으로 추측
- "일반" 개체 분류 데이터 세트에서는 모든 경우에 제로샷 CLIP 더 우세
↔ 반대로 분류 잘 못한 경우를 보면 구체적, 복잡한 테스크 (위성 이미지 분류, 림프절 종양 탐지 등)

- 제로샷이 원샷보다 성능이 높음
- 첫째, CLIP의 제로샷 분류기는 시각적 개념을 직접 지정("소통")할 수 있는 자연어를 통해 생성됩니다. 대조적으로, "정상적인" 지도 학습은 훈련 사례에서 개념을 간접적으로 추론해야 합니다. 문맥 없는 예제 기반 학습은 특히 원샷 사례에서 많은 다른 가설이 데이터와 일치할 수 있다는 단점이 있습니다.
- 제로샷이 다른 16 클래스로 훈련된 (성능이 가장 좋은) 모델의 정확도와 유사한 결과
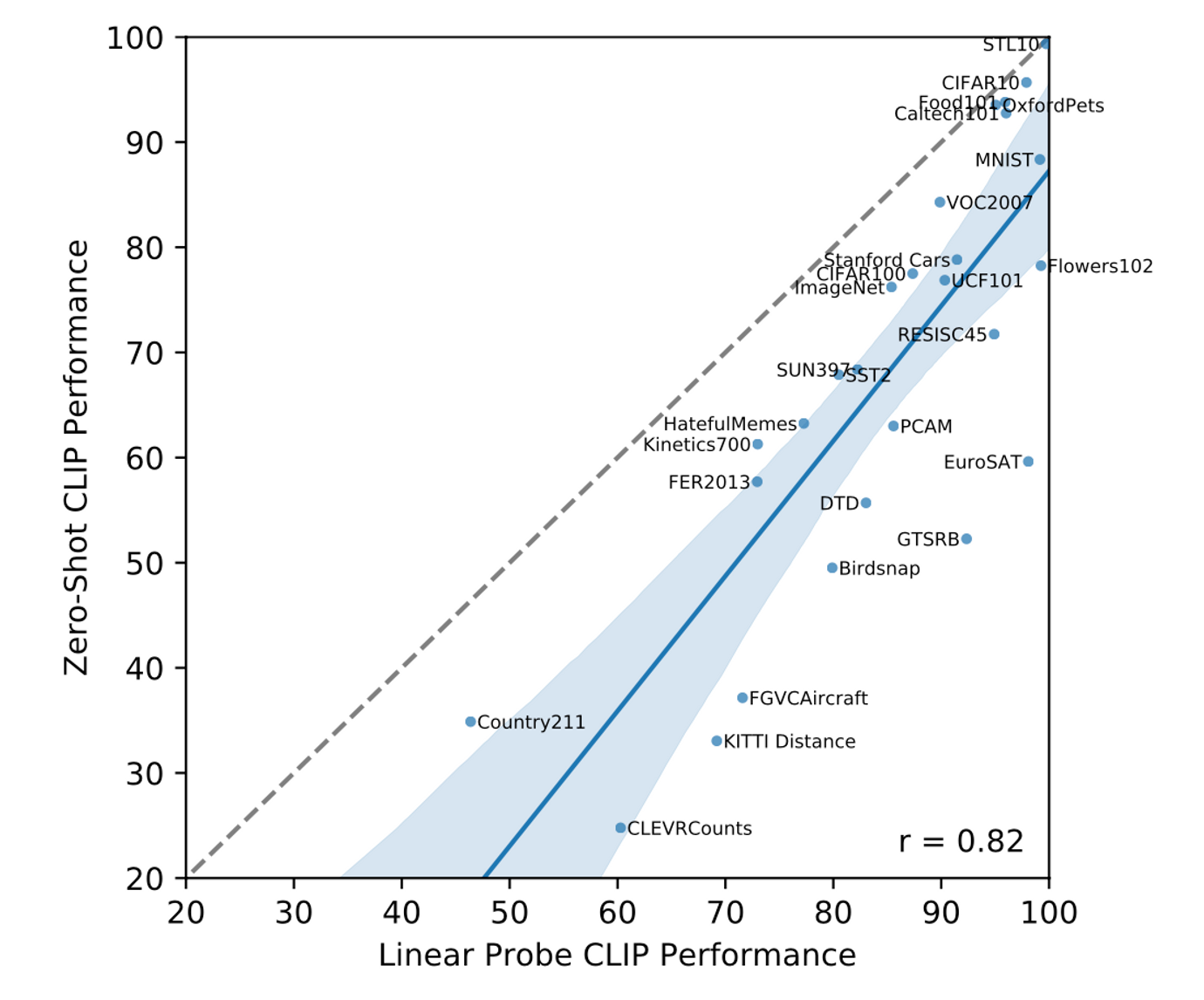
- 완전 지도학습으로 훈련된 모델과의 비교
- 제로샷 성능과 완전히 감독된 성능 사이에는 0.82(p-값 < 10-6)의 양의 상관관계가 있으며, CLIP는 기본 표현과 작업 학습을 제로샷 전송에 연결하는 데 비교적 일관성이 있음

- 훈련컴퓨팅의 증가는 성능 증가에 영향?
- The GPT family of models has so far demonstrated consis- tent improvements in zero-shot performance across a 1000x increase in training compute.
- 해당 관계는 확신할 수 없음.
728x90
'데이터 어쩌구 > 기술 써보기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| XAI (eXplainable AI) 개념 요약 (0) | 2023.09.08 |
|---|---|
| TensorFlow Lite를 이용한 기기 내 대규모 언어모델 탑재 실습 (0) | 2023.09.03 |
| [Paper] A Neural Representation of Sketch Drawings (2017) (1) | 2023.08.28 |
| [Papaer] OFA : Language-Image pretraining model (2022) (0) | 2023.08.28 |
| [NLP] Negative Log Likelihood (0) | 2023.08.28 |


